
Notre-Dame de Paris
Notre-Dame de Paris
by Victor HugoNotre-Dame de Paris is a novel by Victor Hugo published in 1831. The title refers to the Notre Dame Cathedral in Paris, on which the story is centered.
The story begins on Epiphany (6 January), 1482, the day of the Feast of Fools in Paris, France. Quasimodo, a deformed hunchback who is the bell-ringer of Notre Dame, is introduced by his crowning as the Pope of Fools.
Esmeralda, a beautiful Gypsy with a kind and generous heart, captures the hearts of many men, including those of Captain Phoebus a……

Sons and Lovers
Sons and Lovers
by D. H. LawrenceSons and Lovers is a 1913 novel by the English writer D. H. Lawrence. The Modern Library placed it ninth on their list of the 100 best novels of the 20th century. While the novel initially incited a lukewarm critical reception, along with allegations of obscenity, it is today regarded as a masterpiece by many critics and is often regarded as Lawrence's finest achievement.
The third published novel of D. H. Lawrence, taken by many to be his earliest masterpiece, tells the story of Paul Morel, a y……

The Idiot
The Idiot
by Fyodor DostoyevskyThe Idiot is a novel written by the 19th-century Russian author Fyodor Dostoyevsky. It was first published serially in The Russian Messenger between 1868 and 1869. The Idiot is ranked beside some of Dostoyevsky's other works as one of the most brilliant literary achievements of the "Golden Age" of Russian literature.
Prince Lev Nikolayevich Myshkin, a fair-haired young man in his late twenties and a descendant of one of the oldest Russian lines of nobility, arrives in St. Petersburg on a Novembe……

A Pair of Blue Eyes
A Pair of Blue Eyes
by Thomas HardyA Pair of Blue Eyes is a novel by Thomas Hardy, published in 1873, first serialised between September 1872 and July 1873. It was Hardy's third novel, but the first to bear his name on publication.
The book describes the love triangle of a young woman, Elfride Swancourt, and her two suitors from very different backgrounds. Stephen Smith is a socially inferior but ambitious young man who adores her and with whom she shares a country background. Henry Knight is the respectable, established, older m……

Pudd'nhead Wilson
Pudd'nhead Wilson
by Mark TwainPudd'nhead Wilson is an ironic novel by Mark Twain. It was serialized in The Century Magazine (1893-4), before being published as a novel in 1894.
The setting is the fictional Missouri frontier town of Dawson's Landing on the banks of the Mississippi River in the first half of the 19th century. David Wilson, a young lawyer, moves to town and a clever remark of his is misunderstood, which causes locals to brand him a "pudd'nhead" – a nitwit. His hobby of collecting fingerprints does not raise h……

The Woman in White
The Woman in White
by Wilkie CollinsThe Woman in White is an epistolary novel written by Wilkie Collins in 1859, serialized in 1859–1860, and first published in book form in 1860. It is considered to be among the first mystery novels and is widely regarded as one of the first (and finest) in the genre of 'sensation novels'.
The story is considered an early example of detective fiction with the hero, Walter Hartright, employing many of the sleuthing techniques of later private detectives. The use of multiple narratives draws on C……

Three Men in a Boat
Three Men in a Boat
by Jerome K. JeromeThree Men in a Boat (To Say Nothing of the Dog), published in 1889, is a humorous account by English writer Jerome K. Jerome of a boating holiday on the Thames between Kingston and Oxford.
The book was initially intended to be a serious travel guide, with accounts of local history along the route, but the humorous elements took over to the point where the serious and somewhat sentimental passages seem a distraction to the comic novel. One of the most praised things about Three Men in a Boat is h……

The War of the Worlds
The War of the Worlds
by H. G. WellsThe War of the Worlds (1898), a science fiction novel by H. G. Wells, is the first-person narrative of an unnamed protagonist's (and his brother's) adventures in Surrey and London as Earth is invaded by Martians. Written in 1895–97, it is one of the earliest stories that detail a conflict between mankind and an extraterrestrial race. The novel is one of the most commented-on works in the science fiction canon.
The War of the Worlds has two parts, Book One: The Coming of the Martians and Book T……

An Iceland Fisherman
An Iceland Fisherman
by Pierre LotiAn Iceland Fisherman (French: Pêcheur d'Islande, 1886) is a novel by French author Pierre Loti. It depicts the romantic but inevitably sad life of Breton fishermen who sail each summer season to the stormy Iceland cod grounds. Literary critic Edmund Gosse characterized it as "the most popular and finest of all his writings."
Loti's style is a combination of the French realist school, such as Emile Zola, and a form of literary impressionism.[1] As Jules Cambon says, Loti wrote at a "..time when ……

Bleak House
Bleak House
by Charles DickensBleak House is a novel by Charles Dickens, published in 20 monthly instalments between March 1852 and September 1853. It is held to be one of Dickens' finest novels, containing one of the most vast, complex and engaging arrays of minor characters and sub-plots in his entire canon. The story is told partly by the novel's heroine, Esther Summerson, and partly by a mostly omniscient narrator. Memorable characters include the menacing lawyer Tulkinghorn, the friendly but depressive John Jarndyce, an……

He Fell in Love with His Wife
He Fell in Love with His Wife
by Edward Payson RoeThe dreary March evening is rapidly passing from murky gloom to obscurity. Gusts of icy rain and sleet are sweeping full against a man who, though driving, bows his head so low that he cannot see his horses. The patient beasts, however, plod along the miry road, unerringly taking their course to the distant stable door. The highway sometimes passes through a grove on the edge of a forest, and the trees creak and groan as they writhe in the heavy blasts. In occasional groups of pines there is……

The Sorrows of Young Werther
The Sorrows of Young Werther
by Johann Wolfgang von GoetheThe Sorrows of Young Werther (German: Die Leiden des jungen Werthers) is an epistolary and loosely autobiographical novel by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, first published in 1774; a revised edition of the novel was published in 1787. Werther was an important novel of the Sturm und Drang period in German literature, and influenced the later Romantic literary movement.
The six weeks of its intensive writing, in January–March 1774, instantly made the 24-year-old Goethe one of the first internationa……

Mary Barton
Mary Barton
by Elizabeth Cleghorn GaskellMary Barton is the first novel by English author Elizabeth Gaskell, published in 1848. The story is set in the English city of Manchester between 1839 and 1842, and deals with the difficulties faced by the Victorian lower class. It is subtitled 'A Tale of Manchester Life'.
The novel begins in Manchester, where we are introduced to the Bartons and the Wilsons, two working-class families. John Barton is a questioner of the distribution of wealth and the relations between rich and poor. Soon his wi……

The Pickwick Papers
The Pickwick Papers
by Charles DickensThe Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club (also known as The Pickwick Papers) is the first novel by Charles Dickens. He was asked to contribute to the project as an up-and-coming writer following the success of Sketches by Boz, published in 1836 (most of Dickens' novels were issued in shilling instalments before being published in the complete volume). Dickens (still writing under the pseudonym of Boz) increasingly took over the unsuccessful monthly publication after the original illustrator Ro……

Wessex Tales
Wessex Tales
by Thomas HardyWessex Tales is an 1888 collection of tales written by Thomas Hardy, many of which are set before Hardy's birth in 1840.
Through them, Thomas Hardy talks about nineteenth century marriage, grammar, class status, how men and women were viewed, medical diseases and more.
In 1888, Wessex Tales contained only five stories ('The Three Strangers', 'The Withered Arm', 'Fellow-Townsmen', 'Interlopers at the Knap', and 'The Distracted Preacher') all published first in periodicals.
For the 1896 reprinting……

The Diary of a Nobody
The Diary of a Nobody
by George GrossmithThe Diary of a Nobody is an English comic novel written by George Grossmith and his brother Weedon Grossmith, with illustrations by Weedon. The book first appeared in Punch magazine in 1888 – 89, and was first printed in book form in 1892. It is considered a classic work of humour and has never been out of print.
In The Diary of a Nobody the Grossmiths create an accurate, if amusing, record of the manners, customs and experiences of lower-middle-class, suburban Londoners of the late Victorian ……

White Fang
White Fang
by Jack LondonWhite Fang is the titular character and a novel by American author Jack London. First serialized in Outing magazine, it was published in 1906. The story takes place in Yukon Territory, Canada, during the Klondike Gold Rush at the end of the 19th-century, and details a wild wolfdog's journey to domestication. White Fang is a companion novel (and a thematic mirror) to London's best-known work, The Call of the Wild, which is about a kidnapped, domesticated dog embracing his wild ancestry to survive……

Nicholas Nickleby
Nicholas Nickleby
by Charles DickensNicholas Nickleby; or, The Life and Adventures of Nicholas Nickleby is a novel by Charles Dickens. Originally published as a serial from 1838 to 1839, it was Dickens' third novel.
Nicholas Nickleby's father dies unexpectedly after losing all of his money in a poor investment. Nicholas, his mother and his younger sister, Kate, are forced to give up their comfortable lifestyle in Devonshire and travel to London to seek the aid of their only relative, Nicholas's uncle Ralph Nickleby. Ralph, a cold ……

Uncle Tom's Cabin
Uncle Tom's Cabin
by Harriet Beecher StoweUncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in 1852, the novel "helped lay the groundwork for the Civil War", according to Will Kaufman.
Stowe, a Connecticut-born teacher at the Hartford Female Academy and an active abolitionist, featured the character of Uncle Tom, a long-suffering black slave around whom the stories of other characters revolve. The sentimental novel depicts the reality of slavery while also asserting ……

A Bundle of Letters
A Bundle of Letters
by Henry James"A Bundle of Letters" is a comic short story by Henry James, originally published in The Parisian magazine in 1878, which is also when the story takes place. The story is one of James' few ventures into epistolary fiction. As he did so often, especially in the early stages of his career, James made the tale part of his international theme: his letter-writers represent a number of different countries. Although some of the characters look like well-worn stereotypes — the wolfish Frenchman, the p……

Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman
United States (1819-1892)Walter "Walt" Whitman (May 31, 1819 – March 26, 1892) was an American poet, essayist and journalist. A humanist, he was a part of the transition between transcendentalism and realism, incorporating both views in his works. Whitman is among the most influential poets in the American canon, often called the father of free verse. His work was very controversial in its time, particularly his poetry collection Leaves of Grass, which was described as obscene for its overt sexuality.
Born on Long Isl……

Oscar Wilde
Oscar Wilde
Irish (1854-1900)Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 1854 – 30 November 1900) was an Irish writer and poet. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of London's most popular playwrights in the early 1890s. Today he is remembered for his epigrams, his only novel: The Picture of Dorian Gray, his plays and the circumstances of his imprisonment which was followed by his early death.
Wilde's parents were successful Anglo-Irish Dublin intellectuals. Their son became fluent in……

Mark Twain
Mark Twain
American (1835-1910)Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), better known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American author and humorist. He is most noted for his novel The Adventures of Tom Sawyer (1876) and its sequel, Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1885), the latter often called "the Great American Novel."
Twain grew up in Hannibal, Missouri, which would later provide the setting for Huckleberry Finn and Tom Sawyer. He apprenticed with a printer. He also worked as a typesetter and contr……

Robert E. Howard
Robert E. Howard
American (1906-1936)Robert Ervin Howard (January 22, 1906 – June 11, 1936) was an American author who wrote pulp fiction in a diverse range of genres. He is well known for his character Conan the Barbarian and is regarded as the father of the sword and sorcery subgenre. Howard was born and raised in the state of Texas. He spent most of his life in the town of Cross Plains with some time spent in nearby Brownwood.
A bookish and intellectual child, he was also a fan of boxing and spent some time in his late teens b……
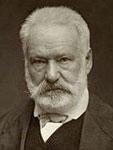
Victor Hugo
Victor Hugo
France (1802-1885)Victor Marie Hugo (26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French poet, novelist, and dramatist. He is considered one of the most well-known French Romantic writers. In France, Hugo's literary fame comes first from his poetry but also rests upon his novels and his dramatic achievements. Among many volumes of poetry, Les Contemplations and La Légende des siècles stand particularly high in critical esteem. Outside France, his best-known works are the novels Les Misérables, 1862, and Notre-Dame ……

Jane Austen
Jane Austen
England (1775-1817)Jane Austen (16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist whose works of romantic fiction, set among the landed gentry, earned her a place as one of the most widely read writers in English literature. Her realism and biting social commentary have gained her historical importance among scholars and critics.
Austen lived her entire life as part of a close-knit family located on the lower fringes of the English landed gentry. She was educated primarily by her father and older brothers……

Thomas Hughes
Thomas Hughes
England (1822-1896)Thomas Hughes (20 October 1822 – 22 March 1896) was an English lawyer and author. He is most famous for his novel Tom Brown's School Days (1857), a semi-autobiographical work set at Rugby School, which Hughes had attended. It had a lesser-known sequel, Tom Brown at Oxford (1861).
Hughes was the second son of John Hughes, editor of the Boscobel Tracts (1830). Thomas Hughes was born in Uffington, Berkshire (now Oxfordshire). He had six brothers, and one sister, Jane Senior who later became Brita……

Marietta Holley
Marietta Holley
American (1836-1926)Marietta Holley (1836-1926), was an American humorist who used satire to comment on U.S. society and politics. Holley was frequently compared to Mark Twain and Edgar Nye.
Holley was born on to John Milton and Mary Tabor on July 16, 1836. She was the youngest of seven children. They lived on a small farm in Jefferson County, NY. At the age of 14, she ended her formal education to make a decent living and help support her family by giving piano lessons to students. When she was 17, she converted t……

Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes
England (1588-1679)Thomas Hobbes of Malmesbury (5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679), in some older texts Thomas Hobbs of Malmsbury, was an English philosopher, best known today for his work on political philosophy. His 1651 book Leviathan established the foundation for most of Western political philosophy from the perspective of social contract theory.
Hobbes was a champion of absolutism for the sovereign but he also developed some of the fundamentals of European liberal thought: the right of the individual; the nat……

George Eliot
George Eliot
English (1819-1880)Mary Anne (alternatively Mary Ann or Marian) Evans (22 November 1819 – 22 December 1880), better known by her pen name George Eliot, was an English novelist, journalist and translator, and one of the leading writers of the Victorian era. She is the author of seven novels, including Adam Bede (1859), The Mill on the Floss (1860), Silas Marner (1861), Middlemarch (1871–72), and Daniel Deronda (1876), most of them set in provincial England and known for their realism and psychological insight.
……

Alexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas
French (1802-1870)Alexandre Dumas (born Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie, 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas, père, was a French writer, best known for his historical novels of high adventure. Translated into nearly 100 languages, these have made him one of the most widely read French authors in the world. Many of his novels, including The Count of Monte Cristo, The Three Musketeers, Twenty Years After, and The Vicomte de Bragelonne: Ten Years Later were originally published as serials.……

Fyodor Dostoevsky
Fyodor Dostoevsky
Russian (1821-1881)Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoyevsky(11 November 1821 – 9 February 1881), sometimes transliterated Dostoevsky, was a Russian novelist, short story writer, and essayist. Dostoyevsky's literary works explore human psychology in the troubled political, social and spiritual context of 19th-century Russia. Although he began writing in the mid-1840s, his most memorable works—including Crime and Punishment, The Idiot and The Brothers Karamazov—are from his later years. His work consists of eleven nove……

Arthur Conan Doyle
Arthur Conan Doyle
British (1859-1930)Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle DL (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a Scottish physician and writer, most noted for his stories about the detective Sherlock Holmes, generally considered milestones in the field of crime fiction, and for the adventures of Professor Challenger. He was a prolific writer whose other works include fantasy and science fiction stories, plays, romances, poetry, non-fiction and historical novels.
Arthur Conan Doyle was born on 22 May 1859 at 11 Picardy Place, Edinburgh, ……

Charles Dickens
Charles Dickens
British (1812-1870)Charles John Huffam Dickens (7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's most memorable fictional characters and is generally regarded as the greatest novelist of the Victorian period. During his life, his works enjoyed unprecedented fame, and by the twentieth century his literary genius was broadly acknowledged by critics and scholars. His novels and short stories continue to be widely popular.
Born in Portsmouth, England, Dickens lef……

Rene Descartes
Rene Descartes
French (1596-1650)René Descartes (31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, mathematician, and writer who spent most of his adult life in the Dutch Republic. He has been dubbed the 'Father of Modern Philosophy', and much subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings, which are studied closely to this day. In particular, his Meditations on First Philosophy continues to be a standard text at most university philosophy departments. Descartes' influence in mathematics is equally app……

Daniel Defoe
Daniel Defoe
English (1660-1731)Daniel Defoe (1660 – 24 April 1731),born Daniel Foe, was an English trader, writer, journalist, pamphleteer and spy, now most famous for his novel Robinson Crusoe. Defoe is notable for being one of the earliest proponents of the novel, as he helped to popularise the form in Britain, and, along with others such as Samuel Richardson, is among the founders of the English novel. A prolific and versatile writer, he wrote more than 500 books, pamphlets and journals on various topics (including polit……

Honore de Balzac
Honore de Balzac
France (1799-1850)Honoré de Balzac (20 May 1799 – 18 August 1850) was a French novelist and playwright. His magnum opus was a sequence of short stories and novels collectively entitled La Comédie humaine, which presents a panorama of French life in the years after the 1815 fall of Napoleon.
Due to his keen observation of detail and unfiltered representation of society, Balzac is regarded as one of the founders of realism in European literature. He is renowned for his multifaceted characters, who are complex, ……

Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
British (1809-1882)Charles Robert Darwin, FRS (12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestors, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding.
Darwin published his theory of evolution with compelling evidence in h……

Stephen Crane
Stephen Crane
American (1871-1900)Stephen Crane (November 1, 1871 – June 5, 1900) was an American novelist, short story writer, poet and journalist. Prolific throughout his short life, he wrote notable works in the Realist tradition as well as early examples of American Naturalism and Impressionism. He is recognized by modern critics as one of the most innovative writers of his generation.
The eighth surviving child of Methodist Protestant parents, Crane began writing at the age of four and had published several articles by th……

Wilkie Collins
Wilkie Collins
English (1824-1889)William Wilkie Collins (8 January 1824 – 23 September 1889) was an English novelist, playwright, and author of short stories. He was very popular during the Victorian era and wrote 30 novels, more than 60 short stories, 14 plays, and more than 100 nonfiction essays. His best-known works are The Woman in White, The Moonstone, Armadale, and No Name.
Collins was a lifelong friend of Charles Dickens. A number of Collins's works were first published in Dickens's journals All the Year Round and Hous……